The Defense Industrial Base is a network of more that 200,000 companies who supply goods and service to the Department of Defense. It includes small businesses, big corporations, and startups. A new report from the Government Accountability Office highlights the risks that the DIB faces, as well as its challenges in addressing these threats.
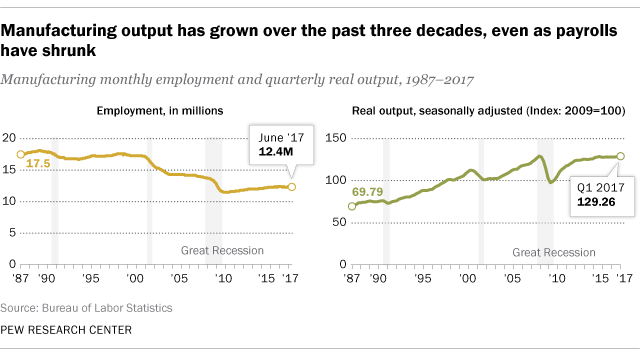
Over the past 10 years, the defense industrial base has declined by nearly 40 percent. This has made it difficult for the Department of Defense to attract new businesses into the sector. The Defense Department has attempted to address this problem by making a range of initiatives to encourage new businesses. Despite these attempts, many smaller firms are being left behind. This has led to a rising national security risk.
Numerous DOD departments are currently working together to reduce risks in the DIB. The department doesn't have a comprehensive strategy to manage these risks. GAO conducted an analysis of several department reports and interviewed DOD representatives to determine where improvements could be made. GAO identified five elements which could help the department reach its goals.
One of the biggest concerns is the loss of commercial suppliers. These businesses supply parts for the Pentagon's weapon systems. There aren't many metrics available to determine how many new companies enter the market. The industry has seen a decline in small-businesses over the past decade.
Other issues include material shortages and reliance on foreign suppliers. Additional problems include intellectual property restrictions that slow down the military's acquisitions process and a lack of standardization for what is considered "new entrant" to the defense industry base.
The GAO recommended that the Department of Defense update its policy on mitigating risks in the DIB. The GAO also recommended that the department continue to engage with traditional defense contractors and to implement tools that will make commercial technology providers more easily enter the DoD market. These recommendations should be part a larger strategy to address concerns about the industrial base.
The Defense Department should examine how its OTAs, CSOs, and other resources can be used to accelerate acquisition strategy development. The supply chain can be restructured to produce dynamic outcomes by using the right people and processes.

Despite the fact that the number has dropped over the past decade in defense industry, it is still developing. Many companies do not feel comfortable with the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR). Furthermore, the current landscape may lead to fewer opportunities for small businesses to compete.
For innovation to take place in the defense industrial base, small businesses and startups are essential. Companies that are part of the resilient DIB can support National Security requirements while allowing the Department of Defense to better develop new and improved military equipment.
The defense industrial base is complex and requires a comprehensive strategy in order to ensure that the resources are available for the military's needs. It is vital that the Department of Defense studies best practices in technology integration to ensure more efficient and innovative products.
FAQ
What skills are required to be a production manager?
A production planner must be organized, flexible, and able multitask to succeed. Also, you must be able and willing to communicate with clients and coworkers.
What are manufacturing & logistics?
Manufacturing is the act of producing goods from raw materials using machines and processes. Logistics manages all aspects of the supply chain, including procurement, production planning and distribution, inventory control, transportation, customer service, and transport. Manufacturing and logistics are often considered together as a broader term that encompasses both the process of creating products and delivering them to customers.
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
A production planner makes sure all project elements are delivered on schedule, within budget, as well as within the agreed scope. They ensure that the product or service is of high quality and meets client requirements.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehouses have become more dependent on automation. E-commerce has brought increased demand for more efficient and quicker delivery times.
Warehouses should be able adapt quickly to new needs. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. Automating warehouses has many benefits. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale more easily
-
Workers are more productive
-
Provides visibility into everything that happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Minimizes downtime and increases uptime
-
Quality products delivered on time
-
Eliminates human error
-
Assure compliance with regulations
Do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes before learning about Logistics?
No. You don't have to know about manufacturing processes before learning about logistics. Knowing about manufacturing processes will help you understand how logistics works.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The major difference between a Production Planner and a Project Manager is that a Project Manager is often the person responsible for organizing and planning the entire project. While a Production Planner is involved mainly in the planning stage,
What are the jobs in logistics?
There are many jobs available in logistics. These are some of the jobs available in logistics:
-
Warehouse workers - They load trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers: They drive trucks and trailers and deliver goods and make pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers – They sort and package freight at warehouses.
-
Inventory managers – They manage the inventory in warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators are responsible for organizing and planning logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service representatives - They answer calls and emails from customers.
-
Shipping clerks: They process shipping requests and issue bills.
-
Order fillers – They fill orders based upon what was ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors - They check incoming and outgoing products for defects.
-
Others - There are many types of jobs in logistics such as transport supervisors and cargo specialists.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma in Manufacturing:
Six Sigma is defined as "the application of statistical process control (SPC) techniques to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department developed it at their Tokyo plant in Japan in 1986. Six Sigma's core idea is to improve the quality of processes by standardizing and eliminating defects. Since there are no perfect products, or services, this approach has been adopted by many companies over the years. Six Sigma's main objective is to reduce variations from the production average. This means that you can take a sample from your product and then compare its performance to the average to find out how often the process differs from the norm. If the deviation is excessive, it's likely that something needs to be fixed.
The first step toward implementing Six Sigma is understanding how variability works in your business. Once you have this understanding, you will need to identify sources and causes of variation. You'll also want to determine whether these variations are random or systematic. Random variations happen when people make errors; systematic variations are caused externally. You could consider random variations if some widgets fall off the assembly lines. If however, you notice that each time you assemble a widget it falls apart in exactly the same spot, that is a problem.
Once you identify the problem areas, it is time to create solutions. The solution could involve changing how you do things, or redesigning your entire process. After implementing the new changes, you should test them again to see if they worked. If they don't work, you will need to go back to the drawing boards and create a new plan.